Attitude, Orbit, Guidance, Navigation Control (AOGNC)
The AOGNC domain in a CDF study will mostly use COMET to design and model their equipment for the spacecraft. The following steps use the example of a Reaction Wheel to be modelled in the Tutorial COMET model:
-
Connect to Citrix and open the COMET Application. To do so, follow the steps outlined here.
-
Connect to the CDF COMET server and open the model
Tutorial COMET. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Also open the model
AOGNC catalogue. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Open the Element Definition browser for both the Study Model and the Catalogue Model. You can do that by following the steps outlined here.
-
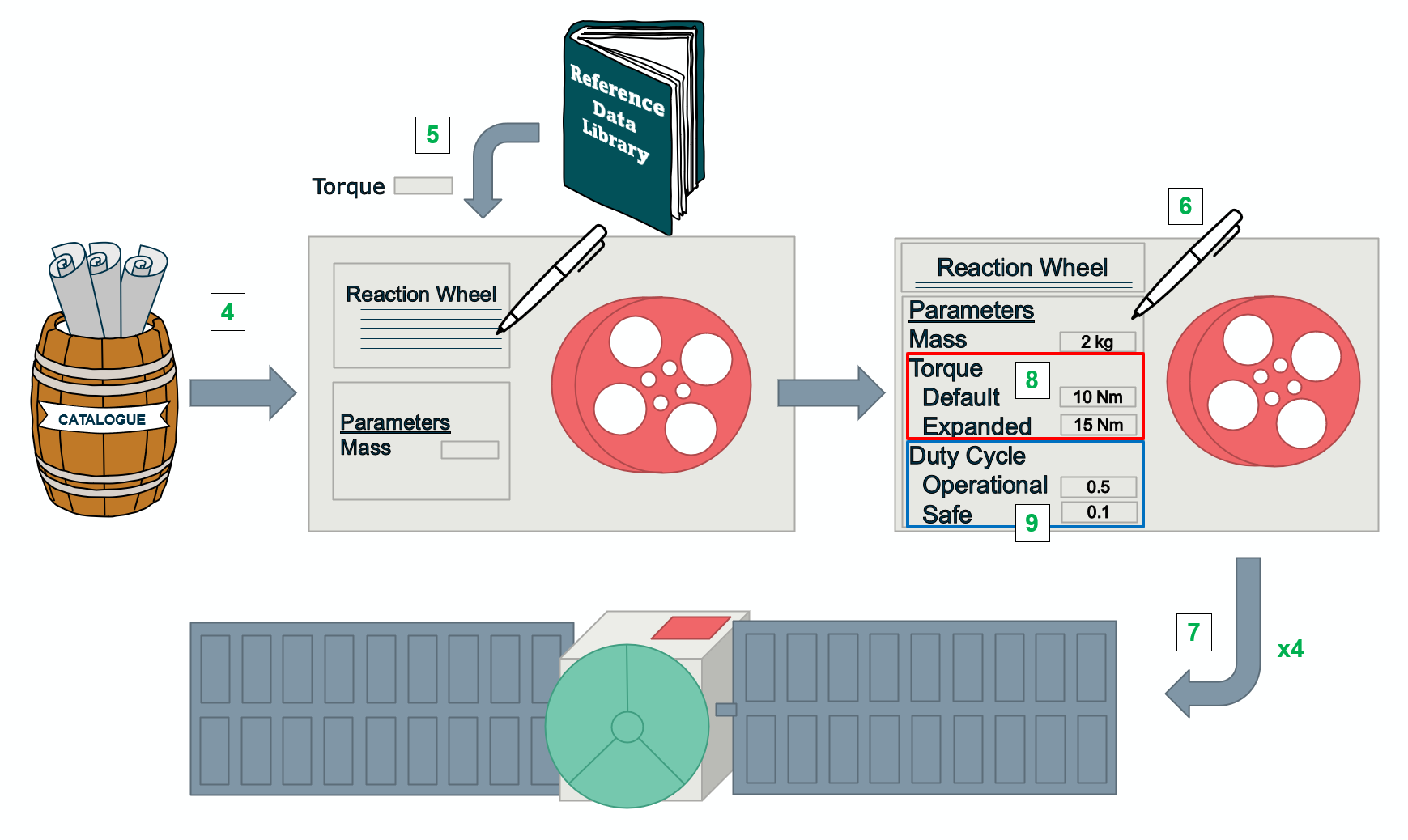
Use the
Generic Equipmentfrom the catalogue to define theReaction WheelElement Definition in theTutorial COMETmodel. To do so, follow the steps outlined here.NOTE: Normally, the Catalogue Model should first be searched to see if there already is an Element Definition describing the equipment in question. In this case, it is assumed this was done and no matching
Reaction Wheelequipment was found. Therefore, this tutorial makes use of theGeneric Equipment -
Use the Reference Data Library to add the additional parameter
torqueto the Element Definition. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Populate the
Manualfields of the Parameter Values for the parametersmass,maturity margin,power while onand the newly createdtorqueparameter. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Create 4 Element Usages of the
Reaction Wheelin theSpacecraftElement Definition. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. - The tutorial model contains 2 Options: the “Default” Option describing the baseline spacecraft design and the “Expanded” Option describing a larger version of the spacecraft with a larger payload. This requires some changes in the AOGNC design:
- The
Reaction Wheelin the “Expanded Option” should have a largertorqueand therefore this parameter needs to be Option dependent. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. - Introduce different values for the
torqueparameter in the two Options. - The “Expanded Option” will also require a 5th
Reaction Wheelinside theSpacecraftwhich is not necessary in the “Default” Option. To do so, follow the steps outlined here.
- The
- Creating a power budget in COMET requires the use of Finite States modelling the system modes of the spacecraft. In this tutorial model only two system modes are defined as Finite States: the Safe Mode and the Operational Mode. To model the varying power consumption of the
Reaction Wheelduring both modes:- Introduce State Dependence to the parameter
power duty cycleof theReaction Wheel. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. - Populate the
power duty cycleparameter by providing values for the different Finite States.
- Introduce State Dependence to the parameter
In the above steps the COMET Application was used to directly interact with the Study Model. However, one of the key advantages of storing data on the COMET server is that it also offers the possibility to interact with the Study Model using standard Excel workbooks and using the COMET server as an interface between the workbooks of the different domains. In the following steps, an overview on how this link between the Study Model and Excel can be achieved with the Excel COMET Plugin is provided. A specific Excel workbook for the AOGNC domain has been set-up by the AOGNC experts from previous CDF studies and should be available in the Study Folder of the CDF Working drive (accessible from Citrix). In this tutorial, for the sake of simplicity, a blank Excel workbook will be used to demonstrate the basic functionality:
-
Use the COMET Application to subscribe to the parameter
wet massof theSpacecraftElement Definition. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. This parameter will be needed for the Excel computations. -
Connect to Citrix and open an instance of Excel with the COMET Excel Plugin. To do so, follow the steps outlined here.
-
In Excel use the COMET Excel Plugin to connect to the CDF COMET server and open the model
Tutorial COMET. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Execute a
Rebuildand find thewet massparameterActual Valuecell in the Parameters sheet. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
On a new sheet in the Excel workbook perform a simplified calculation to compute a value for the
massparameter of theReaction Wheelmaking use of the cell name referring to the Subscription of thewet massparameter. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Attribute a cell name to the result field including the calculated
massparameter. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
In the Parameters sheet insert the cell name as a formula in the
Computedfield of themassparameter and set theSwitchaccordingly. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Use
Submitto “push” the computed value to the Study Model. To do so, follow the steps outlined here. -
Switch back to the COMET Application and verify the new value is introduced in the
massparameter and marked as ready for publication (highlighted in blue).